
On the “Write the changes to disks?” screen, click on the “Continue” button. On the “Installation Type” screen, select “Erase disk and install Ubuntu”. On the next screen, select “Download updates while installing Ubuntu” and “Install third-party software for graphics and Wi-Fi hardware, Flash, MP3 and other media”. Select your language and click on the “Install Ubuntu” button. The virtual machine will now boot from the ISO file and you will be presented with the Ubuntu installation screen. In the “Select start-up disk” window, select the Ubuntu ISO file you downloaded earlier and click on the “Open” button. Once the virtual machine has been created, select it and click on the “Start” button. Click on the “Create” button to create the virtual machine. In the “Storage on physical hard disk” window, select the size of the virtual hard disk.

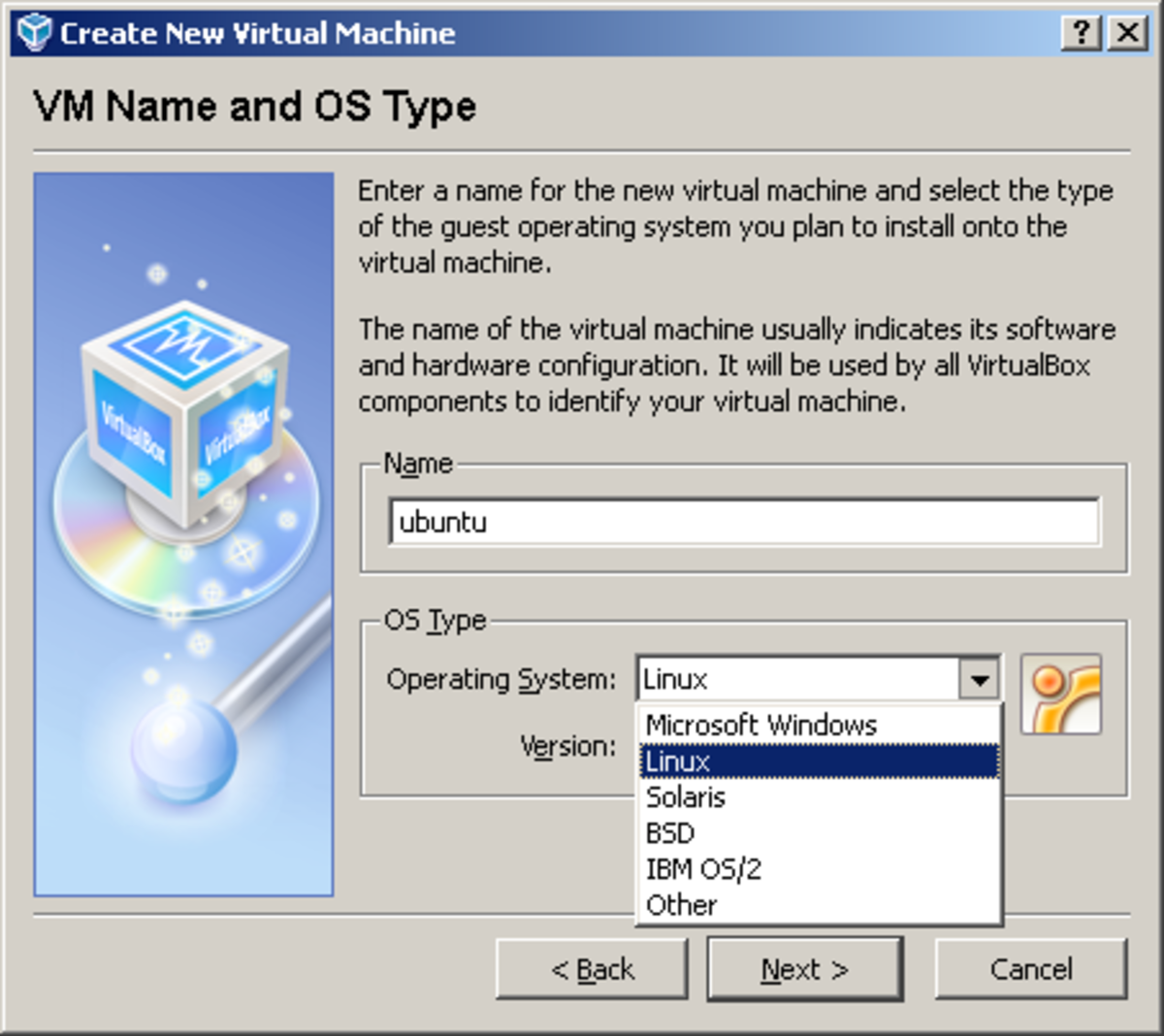
Click on the “Next” button and select “Dynamically allocated”. In the “Create Virtual Disk” window, select “VDI ( VirtualBox Disk Image)”. Click on the “Next” button again and select “Create a virtual hard disk now”. Click on the “Next” button and select the amount of memory you want to allocate for your server. In our case, we will be selecting “Linux” and “Ubuntu (64-bit)”. In the “Create Virtual Machine” window, give your machine a name and select the type of operating system you want to install. To do this, click on the “New” button in the main window. The first step is to create a new virtual machine in VirtualBox. It can also be used for training purposes or for hosting a small website or application. Creating a Linux server in VirtualBox is a great way to test out server administration without having to invest in physical hardware. You can use any other Linux distribution as well, but the steps might be slightly different.

We will be using the Ubuntu Server 18.04 LTS for this tutorial.

In this article, we will show you how to create a Linux server in VirtualBox.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
